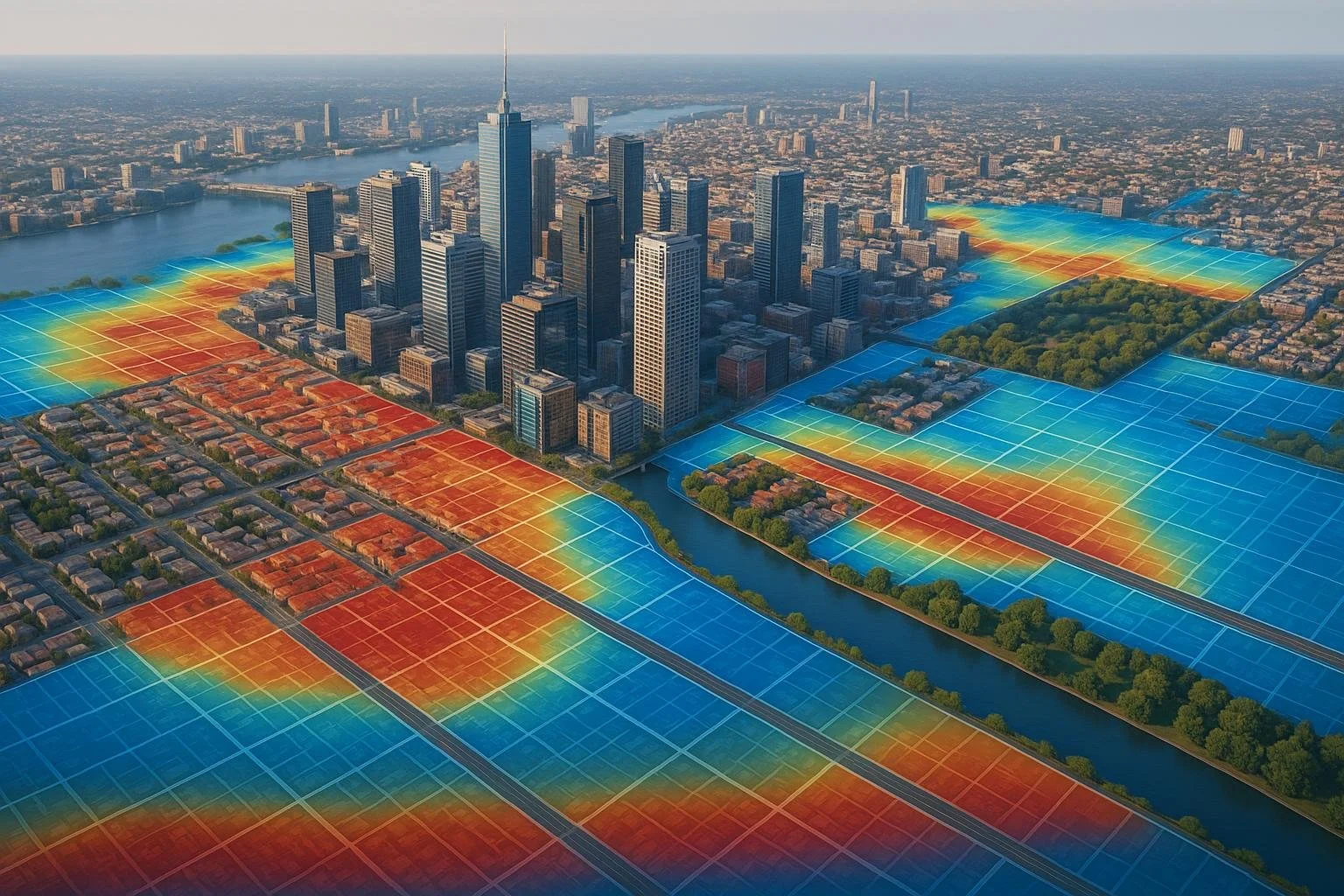
GIS and Heat Mapping for Real Estate Demand Analysis
GIS (Geographic Information Systems) and heat mapping are game changers in real estate. These tools help professionals visualize market trends, identify demand hotspots, and make data-driven decisions with precision. By combining property values, demographics, and market activity into interactive maps, you can spot opportunities and avoid risks.
Key Takeaways:
- GIS: Maps and analyzes spatial data like property values, demographics, and market trends.
- Heat Mapping: Uses color gradients to show demand intensity, pricing trends, or activity levels.
- Applications: Identify high-demand areas, compare neighborhoods, and assess market risks.
- Data Sources: Property sales, demographic stats, amenities, and zoning laws are essential.
- Challenges: Accuracy depends on up-to-date data, and costs or technical expertise may be barriers.
Platforms like CoreCast simplify this process by integrating GIS tools, real-time data, and portfolio tracking into one solution. These tools are essential for staying competitive in a dynamic real estate market.
Real Estate Mapping, Analytics, and Presentations with Site To Do Business | Sponsored by Esri
Key Data Sources for Effective Heat Mapping
Building accurate heat maps for demand analysis hinges on using the right mix of data. The quality and completeness of your data determine how well your maps can highlight market opportunities and pinpoint areas ripe for investment. With the right inputs, you can distinguish emerging neighborhoods from those that might be overlooked.
Essential Data for Real Estate Heat Maps
To create insightful real estate heat maps, certain data inputs are indispensable:
- Property values and recent sales data: This includes listing prices, sale prices, and transaction records, which provide a snapshot of how property values have shifted over time. Mapping these geographically helps identify areas where prices are climbing, holding steady, or dropping.
- Transaction history: Beyond prices, understanding the frequency of sales in an area offers insight into market activity. High transaction volumes often indicate strong demand, while low activity could point to stagnation or limited inventory.
- Demographic trends: Data like population density, median household income, age distribution, and migration patterns offer clues about what drives demand in specific areas. For example, neighborhoods experiencing population growth or rising incomes often signal increasing housing needs.
- Neighborhood amenities and infrastructure: Features like proximity to top-rated schools, parks, retail hubs, public transit, and major employment centers significantly influence property appeal. Including these in your heat maps can highlight areas with strong lifestyle benefits, which often correlate with higher demand and price growth.
- Market context factors: Zoning laws, crime rates, economic indicators, and planned development projects round out the picture. These elements explain why some areas experience strong demand while others lag behind, and they can help uncover emerging opportunities.
Keeping Data Accurate and Up-to-Date
The reliability of your heat maps starts with sourcing data from trustworthy and regularly updated providers, such as county assessor offices, MLS databases, the U.S. Census Bureau, and established third-party aggregators. Knowing how frequently these sources refresh their data is critical for maintaining accurate insights.
Real estate markets are dynamic - property values can shift within weeks, demographic trends evolve yearly, and new developments can transform neighborhoods almost overnight. To stay on top of these changes, it’s essential to update and cross-check your data regularly. This ensures your heat maps reflect current conditions, not outdated snapshots.
The importance of real-time data integration can't be overstated. As Steven Fox, an appraiser with Binyan Kesef, observed, "Their attention to detail ensured my reports were backed by solid data." Real-time platforms that seamlessly combine data from multiple sources can help maintain consistency, reducing the risk of errors and outdated information. This is especially crucial when your analysis informs high-stakes investment decisions.
U.S. Market Data Considerations
When analyzing American markets, local nuances play a big role in refining your data. U.S. analysis often relies on geographic units like ZIP codes and census tracts, which align with how neighborhoods are perceived and how government data is organized.
For consistency, currency should always be displayed in USD, using standard American formatting (commas for thousands, periods for decimals). Property sizes are typically measured in square feet, and distances are expressed in miles to match local conventions.
Regional differences across the U.S. require attention to local data sources and regulations. For instance, the factors driving demand in Manhattan differ significantly from those in suburban Phoenix or rural Montana. Recognizing these variations while maintaining uniform data formats is key to meaningful analysis.
Access to public datasets also varies by location. Some states and cities provide extensive online access to property records, permits, and demographic information, while others may require direct interaction with local offices. Building connections with local data providers and understanding these regional differences is crucial for creating comprehensive heat maps.
Tools like CoreCast simplify this process by consolidating property, demographic, and market data into one platform. Users can layer multiple data points, visualize their portfolio alongside competitors, and generate branded reports - all in one place. This approach not only saves time but also improves the precision of demand analysis by eliminating the need to manually merge data from separate sources.
Using GIS and Heat Maps to Analyze Real Estate Demand
GIS (Geographic Information Systems) and heat maps take raw data and turn it into actionable insights for the real estate market. By visualizing complex datasets, these tools help professionals identify market trends, spot opportunities, and avoid oversaturated areas. The result? Faster, smarter decision-making.
Identifying Demand Hotspots and Opportunity Zones
Heat maps make it easy to spot geographic trends in property values and sales activity. For instance, overlaying recent sales prices on a city map highlights neighborhoods with rising property values as bright spots, while areas with stagnant prices appear cooler. This simple visual tool helps pinpoint where demand is heating up.
Transaction volume heat maps add another layer of clarity. Areas with frequent sales often signal strong buyer interest and liquidity, while low-activity zones might indicate limited inventory or hesitant buyers. By combining price trends with transaction frequency, you can differentiate between genuinely hot markets and those experiencing temporary fluctuations.
These tools also uncover mismatches between market fundamentals and current pricing. For example, a neighborhood with strong demographic growth but lower property values compared to similar areas might be undervalued. On the flip side, areas with high prices but weakening fundamentals could indicate an overheated market.
Combining Data Layers for Deeper Insights
When you layer multiple datasets, you start to see connections that a single dataset might miss. Combining property values, demographics, infrastructure, and economic data creates a fuller picture of market dynamics.
Take multifamily investments as an example. By layering rental rates with population density, age distribution, employment hubs, and transit access, you can identify areas with high rental demand, good connectivity, and limited supply - prime opportunities for investment.
Infrastructure and amenities also play a big role. Schools, parks, retail centers, and transit hubs heavily influence buyer preferences. A heat map showing property appreciation becomes far more valuable when paired with data on proximity to quality schools or new transit projects.
Economic indicators like job growth and employment rates provide the backbone for sustained demand. Layering this data with housing supply trends can reveal markets where demand might outpace new construction, offering insights for strategic investment.
Practical Applications in Real Estate Strategy
The insights from GIS and heat mapping directly inform smart, targeted strategies across all real estate sectors. These tools make site selection, market analysis, and portfolio management more precise and effective.
For residential investments, heat maps can uncover neighborhoods in transition before the changes are widely recognized. For example, you might notice an area attracting young professionals, new businesses, and rising interest - but where property values haven’t yet caught up. Acting early allows investors to secure properties before prices climb.
In commercial real estate, layering foot traffic patterns, demographic data, and competitor locations paints a clearer picture. A retail site that looks promising based on traffic counts alone might reveal issues like market oversaturation or mismatched demographics when additional layers are added.
Portfolio diversification also benefits from these tools. Mapping current holdings against market performance metrics helps identify concentration risks, coverage gaps, and complementary markets to explore.
Risk management improves with spatial analysis as well. Heat maps can highlight areas prone to economic instability, regulatory challenges, or other vulnerabilities. Visualizing these risks alongside your portfolio allows for proactive adjustments to avoid overexposure in problematic markets.
Platforms like CoreCast simplify this process by integrating property data, demographic insights, and competitive intelligence into unified maps. Users can analyze assets, track deal pipelines, and generate location-specific reports, all in one place. This eliminates the need to manually combine data from multiple sources, ensuring your analysis stays up to date with market conditions.
For developers, GIS analysis is invaluable in identifying underserved areas and forecasting demand. By combining population growth projections with existing housing stock, developers can determine the right project size and location to meet market needs without adding to oversupply.
To truly benefit from these tools, it’s essential to update your analysis regularly and combine quantitative data with local market expertise. While technology provides powerful insights, understanding local nuances is key to turning data into successful investment decisions.
sbb-itb-99d029f
Benefits and Challenges of GIS-Based Heat Mapping
GIS-based heat mapping has reshaped how real estate professionals analyze markets, offering powerful tools alongside some notable hurdles. Understanding these trade-offs is crucial for effective implementation.
Benefits of GIS and Heat Maps in Real Estate
Heat maps turn overwhelming datasets into easy-to-understand visuals, making complex information like property values, transaction volumes, and demographic trends more accessible. This visual clarity can uncover patterns that might otherwise be buried in endless spreadsheets.
They also allow for quicker analysis and faster reactions to market shifts. By presenting multiple data layers in one view, heat maps empower professionals to make more informed and confident decisions. For example, investors can use these tools to evaluate portfolios, manage risks, and identify diversification opportunities.
Collaboration is another standout benefit. GIS platforms make it easier to share spatial data and analysis results, fostering better communication among teams, clients, and investors. This shared understanding strengthens alignment and decision-making.
However, alongside these advantages come challenges that need to be addressed to fully leverage the potential of GIS-based heat mapping.
Challenges and Limitations
The effectiveness of GIS-based heat mapping hinges on accurate and up-to-date data. Outdated property records, incomplete demographic stats, or missing transaction data can skew insights, leading to poor decisions.
Another challenge lies in the technical expertise required. Using GIS tools effectively often demands specialized training. Without it, users risk misinterpreting visualizations, such as confusing correlation with causation or oversimplifying complex market dynamics.
Costs and integration are additional hurdles. Setting up a real estate heat map system can range from $5,000 to over $50,000, depending on the complexity of the project, data sources, and desired features [4]. Adding to the complexity, data integration from multiple sources - each with its own format and update schedule - can be a logistical headache. Compliance with privacy regulations further complicates matters.
Comparing Benefits and Challenges
The interplay between the benefits and challenges of GIS-based heat mapping can guide decisions on whether and how to implement these tools effectively:
| Benefit | Challenge | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Clear visual insights | Reliance on data accuracy | Insights are only as good as the data behind them |
| Better decision-making | Need for technical skills | Specialized training may be required |
| Portfolio risk management | Risk of oversimplification | Visuals can mask complex trends |
| Enhanced collaboration | High costs and integration issues | Advanced systems can be expensive and complex |
Balancing these factors is essential for success. While the advantages often outweigh the drawbacks, achieving reliable results depends on maintaining high-quality data, investing in training, and carefully interpreting visualizations. Professionals must weigh the costs of implementation and training against the potential for improved investment outcomes and operational efficiency.
Platforms like CoreCast aim to address many of these challenges. By offering an all-in-one solution for GIS mapping, portfolio analysis, and real-time data tracking, CoreCast minimizes technical and integration barriers while maintaining the analytical depth that makes heat mapping such a valuable asset for real estate professionals.
Using GIS and Heat Mapping with CoreCast
CoreCast brings GIS and heat mapping tools together in one place, eliminating the need to juggle multiple software solutions or data sources. By centralizing these tools, CoreCast offers a streamlined platform for spatial analysis and demand forecasting, making it a go-to solution for real estate professionals.
CoreCast's Role in Real Estate Demand Analysis
CoreCast serves as an all-in-one real estate intelligence platform, addressing the technical and integration hurdles that often complicate GIS implementation. It seamlessly combines GIS mapping with underwriting tools, deal pipeline tracking, and portfolio analysis, creating a unified workflow tailored to real estate needs.
With CoreCast, users can explore property locations, demand hotspots, and market trends through interactive, U.S.-formatted maps. This functionality builds on the earlier-discussed benefits of GIS and heat mapping, offering actionable insights within a single interface.
One standout feature is the Pipeline Tracker, which maps and lists properties at various stages, from pursuit to sale. This tool helps users visualize opportunities geographically and assess the competitive landscape. By toggling between datasets and forecasts, users can quickly evaluate asset potential and market demand with precision.
For example, a multifamily investor can overlay rental trends, population growth, and competitor data to identify high-demand neighborhoods with limited competition.
Key Features for Heat Mapping and Insights
CoreCast's mapping tools go far beyond simple property visualization. Users can analyze property values, transaction volumes, demographic trends, competitor locations, and market saturation - all within the same platform. The ability to layer data such as recent sales, rental rates, population growth, and neighborhood boundaries provides a detailed view of market dynamics and demand drivers.
The real-time mapping feature enables investors to monitor market shifts as they happen, track portfolio distribution across regions, and compare performance geographically. This helps users uncover emerging opportunities, steer clear of oversaturated areas, and refine investment strategies using the latest spatial intelligence. Automated updates ensure that data remains current and reliable.
By integrating heat maps with demographic, economic, and property data, CoreCast pinpoints areas with rising demand, limited competition, or undervalued assets. Users can overlay multiple data sets - like income levels, housing supply, and competitor density - to identify promising zones for acquisition or development.
CoreCast prioritizes data accuracy by sourcing information from trusted U.S. real estate databases and allowing users to import their own verified data for custom analyses. Regular updates ensure the platform reflects the latest market conditions.
The platform also supports detailed portfolio analysis, enabling users to create custom summaries and evaluate the past performance and future potential of any asset combination. When paired with spatial data, this analysis uncovers geographic patterns and market trends, offering deeper insights into asset performance.
Future Features with CoreCast
CoreCast is set to expand its capabilities even further. Upcoming features include AI-driven automation for predictive analytics, allowing users to forecast market trends and spot emerging demand patterns ahead of the competition.
Advanced reporting tools are also in the works, designed to generate polished, branded reports that incorporate heat mapping and spatial analysis. These reports will make complex geographic data more accessible to stakeholders like investors and lenders, even if they lack technical GIS expertise.
Additionally, CoreCast plans to integrate with property management systems while staying focused on its role as an intelligence and analysis platform - not a property management tool. This integration will give users access to operational data, enhancing both spatial analysis and demand forecasting.
Other planned upgrades include construction management and investor relations features, aimed at providing deeper insights and simplifying workflows. These additions will further solidify CoreCast as a comprehensive solution for real estate intelligence while maintaining the analytical depth that makes heat mapping so valuable.
Beta pricing starts at $50 per user per month, with three tiers available: Free, Essentials at $75, and Pro at $100. This tiered structure ensures that advanced GIS and heat mapping tools are accessible to real estate professionals across different scales of operation.
Conclusion: Real Estate Insights with GIS and CoreCast
GIS and heat mapping have transformed how real estate professionals evaluate market demand across the U.S. By converting intricate data into easy-to-understand visuals, these tools help investors, developers, and agents pinpoint high-demand areas, monitor market shifts, and make smarter investment choices [1][2][3]. Interactive maps that combine property values, demographic trends, and competitor locations uncover patterns that traditional spreadsheets simply can't match.
These technologies empower quicker, more confident decisions by shedding light on supply-demand gaps and competitive dynamics. For example, one real estate investment firm used heat mapping to layer property values, rental demand, and competitor density across several cities. This approach uncovered an underserved neighborhood, leading to a highly profitable acquisition [1][2]. Stories like this highlight how heat mapping can directly influence market strategies.
That said, making the most of these tools requires overcoming challenges like ensuring high-quality data, smooth integration, and technical know-how [2][3]. This is where an all-in-one solution becomes crucial. CoreCast streamlines GIS mapping, portfolio analysis, and deal tracking into a single platform, eliminating the need for fragmented tools and keeping data up-to-date.
CoreCast also simplifies deal management, allowing users to track progress at every stage and create branded reports for stakeholders. As Clay Heighten, Principal at Caddis Healthcare RE, shared:
"They have seamlessly provided the expertise and support we needed to streamline our operations and make smarter, data-driven decisions."
Looking ahead, CoreCast plans to introduce AI-powered automation and advanced reporting features, making real estate demand analysis even more efficient. These advancements will ensure that GIS and heat mapping tools remain accessible and practical for professionals at every level.
With GIS technology and platforms like CoreCast, real estate professionals gain a clear edge. By staying ahead of trends, reducing risks, and delivering stronger results for clients and stakeholders, these tools redefine how the industry approaches market analysis [1][2][3].
FAQs
How can GIS and heat mapping help identify real estate investment opportunities?
GIS and heat mapping offer dynamic ways to analyze real estate market demand. By mapping out data like population density, income levels, and property trends, these tools reveal areas ripe for investment. They simplify spotting patterns, comparing locations, and pinpointing up-and-coming markets.
Platforms such as CoreCast take this a step further by integrating GIS and heat mapping with real-time data analysis. This allows users to assess property performance, monitor deal pipelines, and understand competitive landscapes - all from a single platform. This integrated approach empowers investors to make smarter, data-driven decisions.
What challenges can arise when using GIS-based heat mapping for real estate demand analysis?
GIS-based heat mapping offers incredible insights for real estate demand analysis, but it’s not without its hurdles. A major challenge lies in the accuracy and availability of data. If datasets are outdated or incomplete, the resulting insights can be unreliable. That’s why it’s crucial to vet data sources and ensure they’re updated regularly.
Another obstacle is the technical expertise required to navigate GIS tools effectively. These tools come packed with advanced mapping and analysis features, but interpreting the results or customizing maps often demands specialized skills. For teams without a GIS expert, this can be a significant roadblock.
Finally, there’s the issue of integration with other systems. For instance, combining GIS heat maps with financial models or property management data can be tricky. Seamless integration is key to creating a comprehensive view. Platforms like CoreCast address this by merging various tools and offering an integrated mapping feature tailored for real estate professionals.
How does CoreCast use GIS and heat mapping to enhance real estate demand analysis?
CoreCast uses GIS (Geographic Information Systems) and heat mapping tools to deliver insightful visuals of real estate market demand. By displaying data on an interactive map, users can pinpoint areas with high demand, monitor competitors, and make informed investment choices.
These features help real estate professionals examine trends across different asset classes, spot patterns in property performance, and evaluate market potential with accuracy. CoreCast simplifies the decision-making process, offering a clear view of market dynamics - all within a single platform.

